
Overview
The sensor consists of an IR LED and a photo sensor (phototransistor). The light emitted by the IR LED gets reflected by any object placed in front of the sensor and this reflection is detected by the photo sensor (phototransistor). Any white (or lighter) colored surface reflects more than black (or darker) colored surface.
When the reflected light is detected, it produces Digital HIGH (or Binary 1) output on the Sig pin. The on-board LED indicator will also glow. If no reflection is detected or if the object is too far from the sensor, the output on the SIG pin stays at Digital LOW (Binary 0). The on-board LED indicator will be off as well.
The detectable range of this sensor is 4–16 mm. The module incorporates a Rail-to-Rail Operational Amplifier to amplify the output of phototransistor. There is a potentiometer which can be used to adjust the gain of the amplifier, that is, sensitivity of detection.
Get Inspired
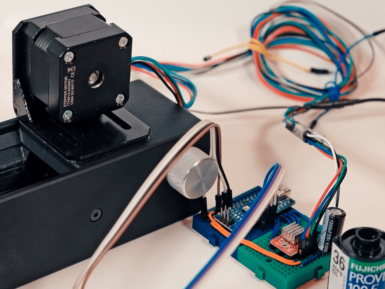
While taking photos today is normally a digital affair, there is a wealth of visual information stored on film negatives. Digitization is possible, but it tends to be rather time-intensive, so photographer/hacker Seckin Sinan Isik decided to automate the process. His setup uses a film carrier augmented with a stepper motor and belt drive to advance the 35mm film under a tripod-mounted digital camera. This is controlled by an Arduino Nano, with the camera’s view shown via a video capture device on a nearby computer. In one mode, the user can adjust the film position semi-manually using pushbuttons, then scan the negative. The whole process can also be automated, with a Python computer vision routine. More details on the project can ben found in Isik's PetaPixel article here.







