
Grove - Hall Sensor
Sold outThe Hall sensor uses the Hall Effect, which is the production of a voltage difference across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and a magnetic field perpendicular to the current.
Overview
There is a continuous-time switch on this Grove module. The output from the module switches from low (turns on) when a magnetic field (south polarity) is perpendicular to the Hall sensor and when it passes the operate point threshold BOP it switches to high (turns off) when the magnetic field disappears.
The twig can for example be used to measure RPM of a wheel or a motor.
Features
- Grove Compatible Interface
- 400ns transition period for rise and fall.
- Continuous-time hall effect sensor
- Reverse current protection
Tech specs
Specifications
|
Item |
Min |
Typical |
Max |
Unit |
|
Supply Voltage |
3.8 |
5.0 |
24 |
V |
|
Supply Current |
4.1 |
- |
24 |
mA |
|
Operating Temperature |
-40 |
- |
85 |
ºC |
Get Inspired
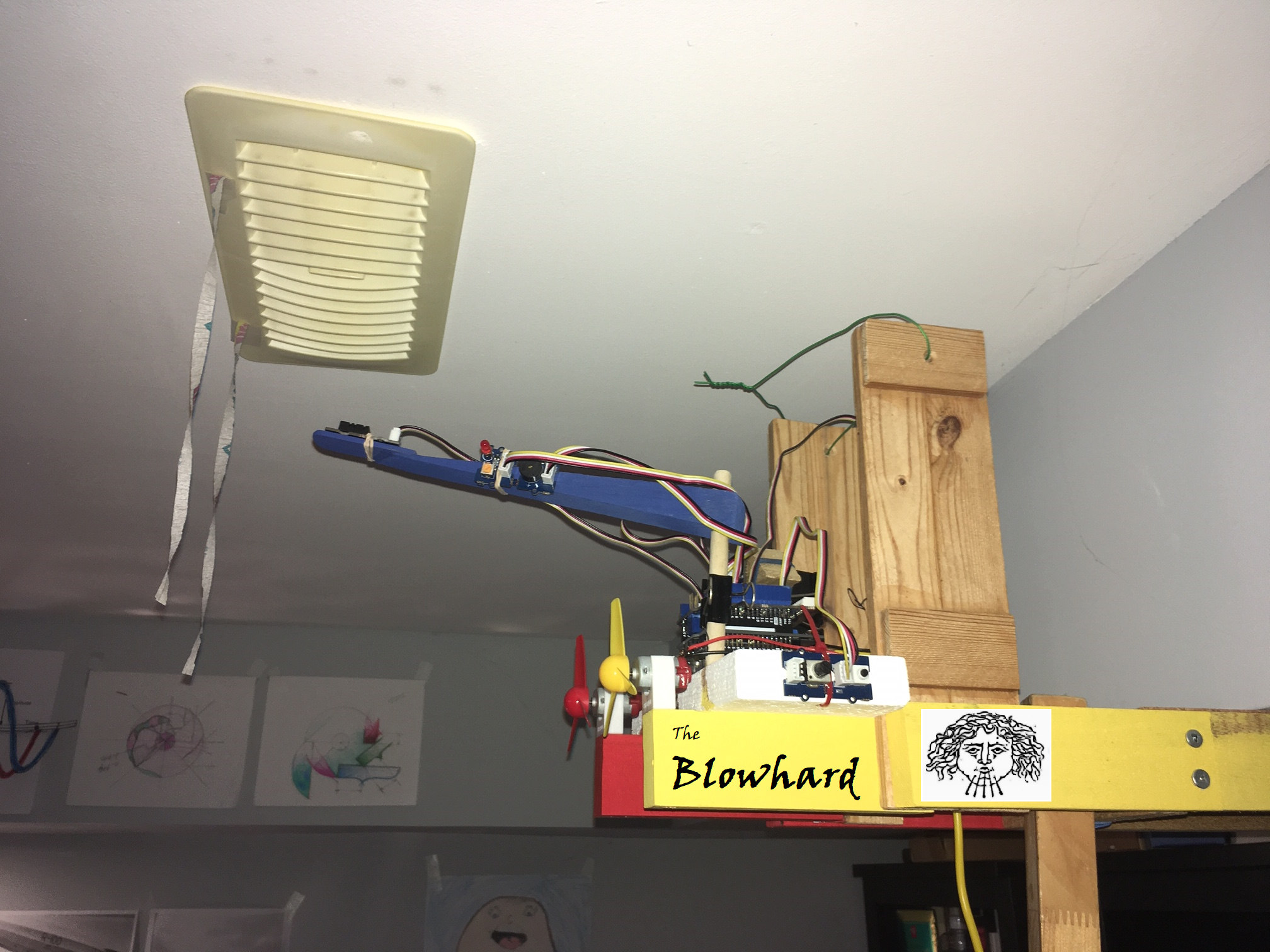

Rate-of-Rise triggered axial fan blowers to improve warm air circulation in a room with one HVAC inlet vent
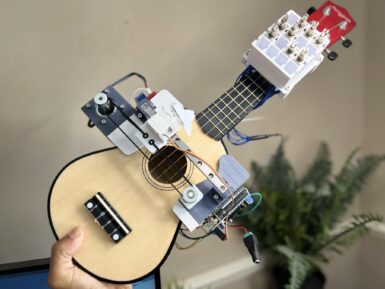
The ukulele has a bit of a reputation for being quaint, but it is a legitimate instrument like any other and that means it takes a lot of practice to play competently. Zeroshot is too busy building cool stuff to bother with all of that, so he put his skills to use constructing this robotic ukulele that plays itself. Like a guitarist, a ukulelist can play a note by strumming multiple strings at once or by picking individual strings. More exotic techniques are also possible, but uncommon and outside the scope of this project. The key to Zeroshot’s design is the mechanism that can both pick and strum. It does so by using two actuators: a servo motor to lift and drop the pick, and a stepper to slide the pick back and forth perpendicular to the strings. An Arduino UNO Rev3 board controls those motors through a HiLetgo L293D motor shield, with a TMC2208 driver module for the stepper. The Arduino can lower the pick and strum it across all of the strings, or it can move to a specific string and pluck just that one. But it would be limited to only a handful of songs if it could only play open strings, so Zeroshot also needed to add hardware to hold the strings down on the fretboard. He chose solenoids for that job, held in a 3D-printed mount. With power coming from the motor shield, the Arduino can extend the solenoids to play any required notes. Zeroshot designed the mount to accommodate up to 16 solenoids, for the first four frets across the four strings. When including open strings, that would give the robot up to 20 notes to work with. But a lot of songs only require a handful of solenoids, as Zeroshot demonstrated by performing Celine Dion’s “My Heart Will Go On.”






