Arduino MKR IMU Shield
Need to integrate inertial measurements within your MKR based project? Plug in the Arduino MKR IMU shield and get the three-dimensional acceleration, yaw rate and magnetic field strength data in 3 perpendicular axes.
Overview
The MKR IMU Shield is based on the BNO055 absolute orientation sensor from Bosch Sensortec GmbH which integrates a triaxial 14-bit accelerometer, a triaxial 16-bit gyroscope with a range of ±2000 degrees per second and a triaxial geomagnetic sensor with a 32-bit microcontroller running the BSX3.0 FusionLib software. The sensor features three-dimensional acceleration, yaw rate and magnetic field strength data each in 3 perpendicular axes.
Tech specs
|
Sensor |
BNO055 from Bosch (product page) |
|
Operating voltage |
3.3V |
|
Extension interface |
4 pin header connector |
|
Communication protocol |
I2C |
|
Compatibility |
MKR Family |
Conformities
Resources for Safety and Products
Manufacturer Information
The production information includes the address and related details of the product manufacturer.
Arduino S.r.l.
Via Andrea Appiani, 25
Monza, MB, IT, 20900
https://www.arduino.cc/
Responsible Person in the EU
An EU-based economic operator who ensures the product's compliance with the required regulations.
Arduino S.r.l.
Via Andrea Appiani, 25
Monza, MB, IT, 20900
Phone: +39 0113157477
Email: support@arduino.cc
Documentation
OSH: Schematics
The Arduino MKR IMU Sheld is open-source hardware! You can build your own board using the following files:
EAGLE FILES IN .ZIP SCHEMATICS IN .PDFLearn more
Get Inspired
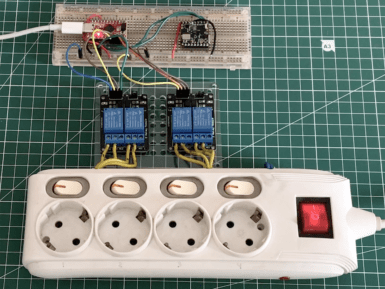
As Jallson Suryo discusses in his project, adding voice controls to our appliances typically involves an internet connection and a smart assistant device such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant. This means extra latency, security concerns, and increased expenses due to the additional hardware and bandwidth requirements. This is why he created a prototype based on an Arduino Nicla Voice that can provide power for up to four outlets using just a voice command. Suryo gathered a dataset by repeating the words “one," “two," “three," “four," “on," and “off” into his phone and then uploaded the recordings to an Edge Impulse project. From here, he split the files into individual words before rebalancing his dataset to ensure each label was equally represented. The classifier model was trained for keyword spotting and used Syntiant NDP120-optimal settings for voice to yield an accuracy of around 80%. Apart from the Nicla Voice, Suryo incorporated a Pro Micro board to handle switching the bank of relays on or off. When the Nicla Voice detects the relay number, such as “one” or “three," it then waits until the follow-up “on” or “off” keyword is detected. With both the number and state now known, it sends an I2C transmission to the accompanying Pro Micro which decodes the command and switches the correct relay. To see more about this voice-controlled power strip, be sure to check out Suryo’s Edge Impulse tutorial.




