
Overview
Based on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi transceiver module and the CH340 USB converter chip, this compact (Open Source) development and prototyping board is ideal for IoT applications.
The Wi-Fi module is compatible with the 802.11 b/g/n standard at 2.4 GHz, has an integrated TCP/IP stack, 19.5 dBm output power, data interface (UART / HSPI / I2C / I2S / Ir Remote Control GPIO / PWM) and PCB antenna.
It also has a micro USB connector and reset button. Programmable with Arduino IDE, it includes interpreters for processing commands for languages such as LUA.
Tech specs
- Model: ESP8266-12E
- Wireless Standard: 802.11 b/g/n
- Frequency range: 2.4 GHz - 2.5 GHz (2400M-2483.5M)
- Wi-Fi mode: Station / SoftAP / SoftAP+station
- Stack: Integrated TCP/IP
- Output power: 19.5dBm in 802.11b mode
- Data interface: UART / HSPI / I2C / I2S / Ir
- Remote Control GPIO / PWM
- Supports protection mode: WPA / WPA2
- Encryption: WEP / TKIP / AES
- Power supply: from 4.5 VDC to 9 VDC (VIN) or via micro USB connector
- Consumption: with continuous Wi-Fi transmission about 70 mA (200 mA MAX) - in standby < 200µA
- Operating temperature: from -40°C to +125°C
- Dimensions (mm): 58×31.20×13
- Weight: 10 grams
Conformities
Get Inspired
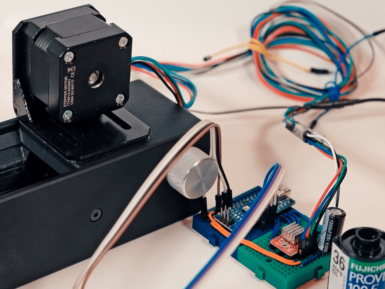
While taking photos today is normally a digital affair, there is a wealth of visual information stored on film negatives. Digitization is possible, but it tends to be rather time-intensive, so photographer/hacker Seckin Sinan Isik decided to automate the process. His setup uses a film carrier augmented with a stepper motor and belt drive to advance the 35mm film under a tripod-mounted digital camera. This is controlled by an Arduino Nano, with the camera’s view shown via a video capture device on a nearby computer. In one mode, the user can adjust the film position semi-manually using pushbuttons, then scan the negative. The whole process can also be automated, with a Python computer vision routine. More details on the project can ben found in Isik's PetaPixel article here.






