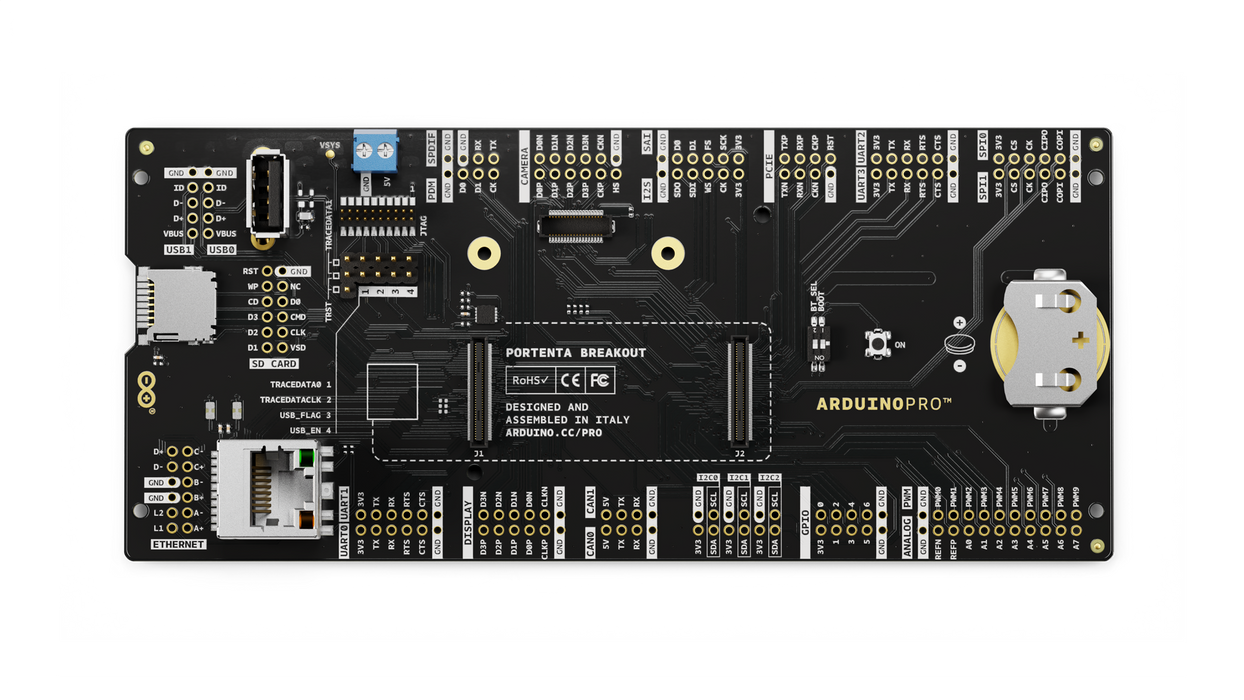
Overview
Portenta Breakout board is designed to help hardware engineers and makers to prototype and help test devices connections and capacity within the Portenta family boards (e.g. the Portenta H7).
It makes all high-density connectors’ signals individually accessible, making it quick and easy to connect and test external hardware components and devices as normally needed during development in the lab.
Target areas
Prototyping
Application examples
This product is designed to work alongside the Portenta family. Please check the Getting Started guide of your Portenta board.
Product Development: The Portenta Breakout board reduces development time for industrial grade solution automation based on the Portenta line.
Technical Education: The Portenta Breakout board can act as the first point of entry for technician education in industrial grade control and embedded systems.
Features
- Power ON Button
- Boot mode DIP switch
- Connectors
- USBA
- RJ45 up to 1Gb/s
- Micro SD card
- MIPI 20T JTAG with trace capability - Power
- CR2032 RTC Lithium Battery backup
- External power terminal block - I/O
- Break out all Portenta High Density connector signals
- Male/female HD connectors allow interposing breakout between Portenta and shield to debug signals - Compatibility
- Standard Portenta High Density connector pinout - Safety information
- Class A
Tech specs
| USB port | USBA |
| Ethernet | RJ45 up to 1Gb/s (Supported on Portenta X8 only) |
| Memory slot | Micro SD card |
| Debug | MIPI 20T JTAG with trace capability |
| Connectors | HD male/female |
| RTC power battery | CR2032 |
| Length | 164 mm |
| Width | 72 mm |
| Weight | 0,069 Kg |
Conformities
Resources for Safety and Products
Manufacturer Information
The production information includes the address and related details of the product manufacturer.
Arduino S.r.l.
Via Andrea Appiani, 25
Monza, MB, IT, 20900
https://www.arduino.cc/
Responsible Person in the EU
An EU-based economic operator who ensures the product's compliance with the required regulations.
Arduino S.r.l.
Via Andrea Appiani, 25
Monza, MB, IT, 20900
Phone: +39 0113157477
Email: support@arduino.cc
Documentation
Study how the Portenta Breakout Carrier works using following files:
Pinout Diagram
Learn more about the portenta's pinout by reading the pinout documentation.
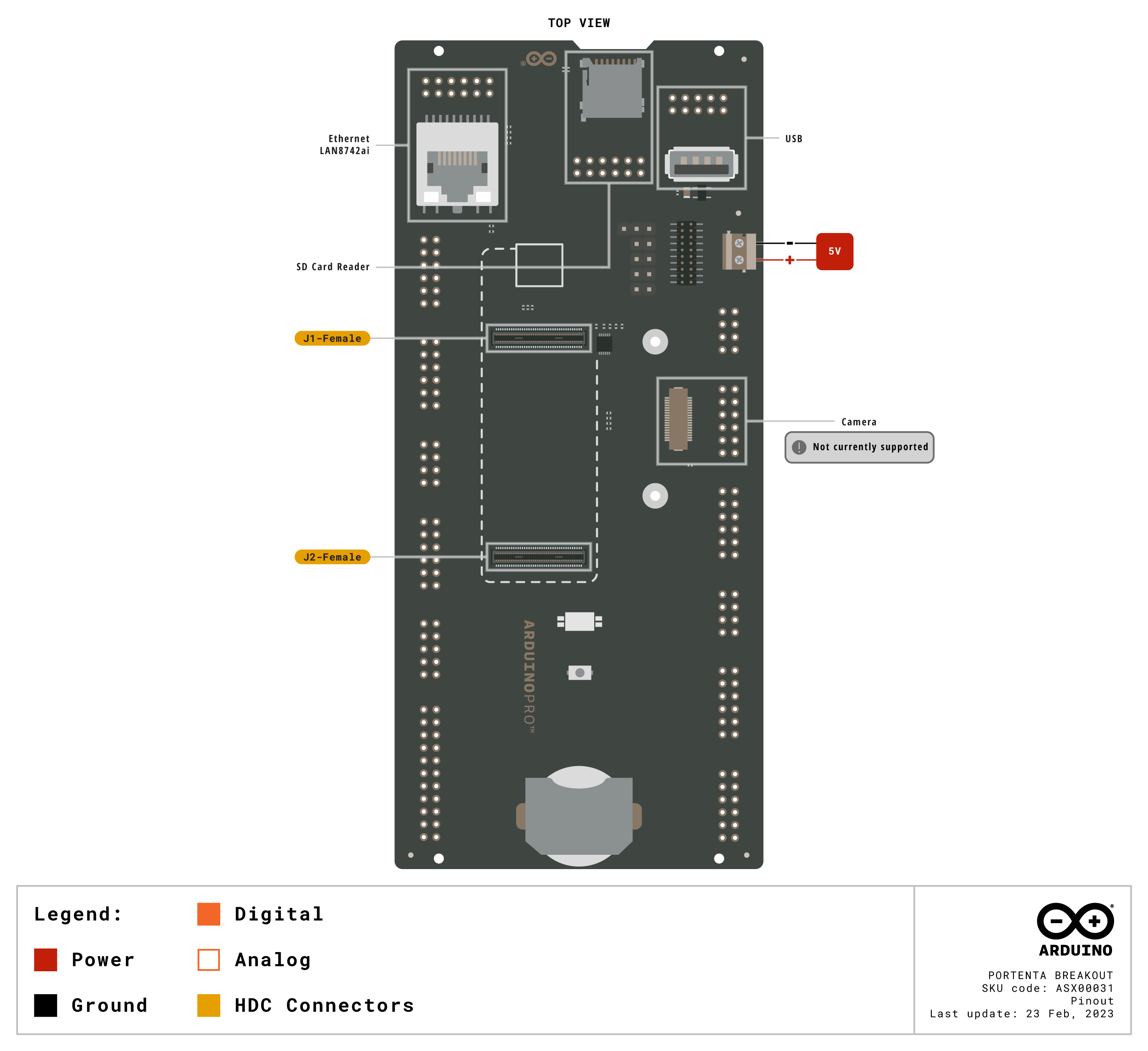
Download the full pinout diagram as PDF here.
Interactive Board Viewer
Learn more
Get Inspired
If you’re interested in embedded machine learning (TinyML) on the Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense, you’ll have found a ton of on-board sensors — digital microphone, accelerometer, gyro, magnetometer, light, proximity, temperature, humidity and color — but realized that for vision you need to attach an external camera. In this article, we will show you how to get image data from a low-cost VGA camera module. We’ll be using the Arduino_OVD767x library to make the software side of things simpler. Hardware setup To get started, you will need: Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense with headersOV7670 CMOS VGA Camera Module 16x female to female jumper wiresA microUSB cable to connect to your Arduino You can of course get a board without headers and solder instead, if that's your preference. The one downside to this setup is that (in module form) there are a lot of jumpers to connect. It’s not hard but you need to take care to connect the right cables at either end. You can use tape to secure the wires once things are done, lest one comes loose. You need to connect the wires as follows: Software setup First, install the Arduino IDE or register for Arduino Create tools. Once you install and open your environment, the camera library is available in the library manager. Install the Arduino IDE or register for Arduino CreateTools > Manage Libraries and search for the OV767 libraryPress the Install button Now, we will use the example sketch to test the cables are connected correctly: Examples > Arduino_OV767X > CameraCaptureRawBytesUncomment (remove the //) from line 48 to display a test pattern Compile and upload to your board Your Arduino is now outputting raw image binary over serial. To view this as an image we’ve included a special application to view the image output from the camera using Processing. Processing is a simple programming environment that was created by graduate students at MIT Media Lab to make









