
Arduino Certification Bundle: Kit & Exam
Officially certify your knowledge of Arduino in the field of programming and electronics by taking the Arduino Certification exam.
Overview
The Arduino Certification exam + kit bundle includes an Arduino Starter Kit and access to the certification exam.
Developed in consultation with interaction designers and electronic engineering professionals as well as in regards to leading technology curriculum, the Arduino Certification exam assesses skills based upon exercises comprised of practical tasks from the Arduino Starter Kit.
To obtain the certificate, you will be requested to answer 36 questions over a period of 75 minutes.
Purchasing the bundle will grant you the Arduino Starter Kit and an activation code, which can be used to unlock 1 attempt at the Arduino Certification exam.
Purchasing the exam alone costs $30, and grants 1 attempt at the Arduino Certification.
Once the code has been redeemed, you have one year to activate the exam, otherwise the code will become invalid.
The exam is available in English. Spanish, Italian, German and Chinese.
You can try the demo to have a closer look at how the exam will be.
To learn more about the certification process, download now the user guide
To learn more about the Arduino Starter Kit, click here
Tech specs
EXAM SUBJECT AREAS
You will encounter questions that test your knowledge in relation to the following 8 main categories:
- Electricity. Understanding the concepts such as resistance, voltage, power and capacitance,and able to measure and calculate them.
- Reading circuits and schematics. Understanding how electronics are represented visually, and the ability to read and analyze electronic circuits.
- Arduino IDE. Understanding the functionality of the Arduino development environment, serial communication, libraries and errors.
- Arduino Boards. Understanding the constitution and capabilities of an Arduino board and the functions of its different parts.
- Frequency and Duty cycle. Understanding the concepts of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and frequency, and being able to calculate duty cycle.
- Electronic components. Understanding how various electronic components such as LEDs, sensors, buttons and motors work, and how to use them in a circuit.
- Programming syntax and semantics. Understanding the building blocks of the Arduino programming language such as functions, arguments, variables and loops.
- Programming logic. Ability to program various electronic components, read, analyze and troubleshoot Arduino code.
For further questions, contact support here.
Resources for Safety and Products
Manufacturer Information
The production information includes the address and related details of the product manufacturer.
Arduino s.r.l.
Via Andrea Appiani, 25
Monza, MB, IT, 20121
https://www.arduino.cc/
Responsible Person in the EU
An EU-based economic operator who ensures the product's compliance with the required regulations.
Arduino s.r.l.
Via Andrea Appiani, 25
Monza, MB, IT, 20121
Phone: +39 0113157477
Email: support@arduino.cc
Get Inspired
An intelligent device to track moves with responses during an interactive space with mapping, backlight, music and smart sculptures. This project makes use of a machine learning algorithm capable of tracking and detecting moves to identify associated gesture recognition through a microcontroller. Smart sculptures, lighting, music and video projection to trigger with each assigned gesture, creating a powerful AV experience highlighting the incredible potential of TinyML for the performing arts. This allows the corresponding media set Tiny ML in interactive to play when the right move was made because all these elements interact to create a new experience. This allows us to create Interactive installations, these sculptures use a combination of motors, sensors, and other electronics to create an immersive and interactive experience for the viewer. They may include projections, sound, and other sensory elements to create a complete experience.
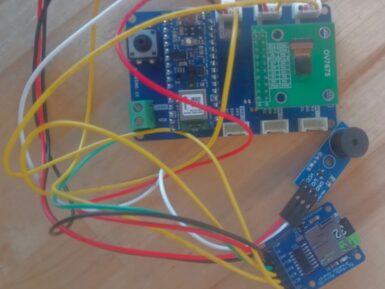
With an array of onboard sensors, Bluetooth® Low Energy connectivity, and the ability to perform edge AI tasks thanks to its nRF52840 SoC, the Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense is a great choice for a wide variety of embedded applications. Further demonstrating this point, a group of students from the Introduction to Embedded Deep Learning course at Carnegie Mellon University have published the culmination of their studies through 10 excellent projects that each use the Tiny Machine Learning Kit and Edge Impulse ML platform. Wrist-based human activity recognition Traditional human activity tracking has relied on the use of smartwatches and phones to recognize certain exercises based on IMU data. However, few have achieved both continuous and low-power operation, which is why Omkar Savkur, Nicholas Toldalagi, and Kevin Xie explored training an embedded model on combined accelerometer and microphone data to distinguish between handwashing, brushing one’s teeth, and idling. Their project continuously runs inferencing on incoming data and then displays the action on both a screen and via two LEDs. Categorizing trash with sound In some circumstances, such as smart cities or home recycling, knowing what types of materials are being thrown away can provide a valuable datapoint for waste management systems. Students Jacky Wang and Gordonson Yan created their project, called SBTrashCat, to recognize trash types by the sounds they make when being thrown into a bin. Currently, the model can three different kinds, along with background noise and human voices to eliminate false positives. Distributed edge machine learning The abundance of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has meant an explosion of computational power and the amount of data needing to be processed before it can become useful. Because a single low-cost edge device does not possess enough power on its own for some tasks, Jong-Ik Park, Chad Taylor, and Anudeep Bolimera have designed a system where








